Esters are derived from a carboxylic acids and an alcohol. Glycerides, which are fatty acid esters of glycerol, are important esters in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids, and making up the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters with low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and found in essential oils and pheromones.
Three basic preparation methods of ester.
1. Reaction of a carboxylate anion with a primary alkyl halide via SN2 reaction.
2.Fischer esterification. Heat a carboxylic acid in an alcohol solvent containing a small amount of strong acid catalyst produces an ester from the alcohol and carboxylic acid.
3.Alcoholysis. Acid chlorides react with alcohols in the presence of pyridine or NaOH to get esters. The reaction is better with less steric bulk.
Reaction of Esters
Esters are hydrolysed by aqueous base (saponification) or aqueous acid (reverse of Fischer Esterification), to yield carbocxylic acids plus alcohols.
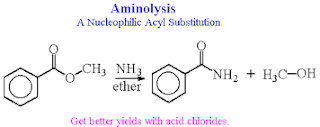
2. Aminolysis ( Conversion of Esters into Alcohols)
Esters react with ammonia and amines to yield amides. The reaction is not often used, however, because higher yields are normally obtained by aminolysis of acid chlorides.
3. Reduction ( Conversion of Esters into Alcohols)
Esters are easily reduced by treatment with LiAIH4 to yield primary alcohols.
4. Reaction of Esters with Grignard Reagent
Esters react with 2 equivalents of a Grignard reagent (RMgX) to yield a tertiary alcohol. The reaction occurs by the usual nucleophilic substitution mechanism to give an intermediate ketone, which reacts further with Grignard reagent to yield a tertiary alcohol.
Facts
Properties and Uses of Esters
Esters are not soluble in water and have a very pleasant smell. Smaller
ones are quite volatile (evaporate easily) and are used in adhesives, inks and
paints. Pentyl ethanoate is used in nail varnish. Many esters are used in flavourings and in perfumes.
Natural fruit flavours also contain blends of esters. Some common
esters in fruit are:
Ester
|
Fruit
|
Pentyl ethanoate
|
Banana
|
Octyl ethanoate
|
Orange
|
Methyl butanoate
|
Pineapple
|
3-Methylbutyl butanoate
|
Apple
|
Which industries might use synthetic esters? Why?
Food Industry
-Flavouring food in particular of lollies & sweets. Also margarine & preservatives.
Cosmetic Industry
-Create nice smelling perfumes and add pleasant aromas to other products such as shampoo and lotions.
Beverage Industry
-To give drinks nice flavours such as cordials.
Alcohol Industry
-Again to add flavour. Most obviously the uses such as Propyl-2-methylpropanoate in Rum.
Medicines
-Especially children's medicines to add nice fruity flavours.
Clothing Industry
-Synthetic fibres such as polyester.
Energy Industry
-Such as to make biodiesel fuels.
Mechanical Industry
-Such as use as lubricants on machinery.